Dogs are born with an instinctive set of postures that can
tell us a lot about their current state of mind. These postures
can vary in intensity and are sometimes even combined. We
can only respond to a dog's behavior appropriately if we can
"read" his body language. Take a look at the examples below:
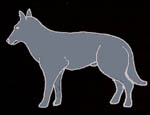
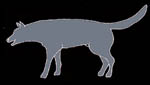
Neutral relaxed position.
The dog stands in a relaxed position with his weight evenly
distributed over his 4 feet. His mouth is usually closed or
just slightly open. His tail hangs down relaxed and his ears
are in an upright position. This is the normal position of
a relaxed and friendly dog.
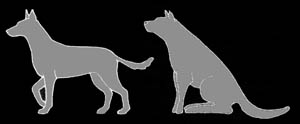
Preparedness Postures.
Alert Posture.
The dog stands in a calm position. His tail is slightly elevated
above his rear. His head is erect and his eyes and ears are
pointed towards the external stimuli. The dog's mouth is closed.
The dog is alert and ready to respond.

Watchful Posture.
The dog sits or stands in a vigilant and tense position
with a slightly open mouth. His head is erect and his ears
are up and pointed forward. The tail is extended backwards.
The dog is ready to flash into action.
Threat and Aggressive Postures.
Impress Posture.
The dog tries to stand as tall as possible. He is holding
his head up high with his ears up and pointed forward. He
is gazing at his opponent, sometimes with his lips lifted
to display teeth. His hackles are up displaying a bristle
from neck to tail. His tail arches high above his back, slightly
waging in a slow and stiff sweeping motion. The dog is aroused
and evaluates the psychological strength of the opponent or
pack mate.
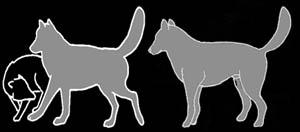
Friend/Foe Evaluation Posture.
The dog stands or walks in a calm but watchful manner. He
holds his head up high with the ears up and pointing forward.
His tense muzzle and lifted lips that display teeth signal
his readiness to respond to any potential threat while his
loosely waging tail slightly elevated above his rear signal
his readiness to greet and interact. The dog does not quite
know how to respond in this situation.

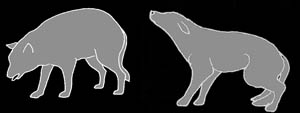
Aggressive Posture.
The dog turns from the Impress Posture into an attack position.
He pushes his head slightly forward and distributes more weight
onto his forelegs. All legs are slightly bent in preparation
for quick movement. His ears are up and he is staring at opponent.
His hackles are up and his stiffened tail is raised just slightly
above his rear. His lips are curled and his teeth are bared,
sometimes snarling. This posture is a dog's last warning before
an attack.

Defensive Aggression Posture.
The dog displays both elements of aggression and fear. He
stands mildly crouched with most of his weight on his rear
legs. His hackles are up (usually from neck to tail) and his
muzzle is tense, wrinkled and snarling with teeth exposed.
The dog's tail is typically tucked under the belly and his
ears are laid back flat against his head. This is the typical
posture of a fear-biter. The dog is afraid and bites out of
fear if approached.

Humility and Fear Postures.
Fear Posture.
The dog ducks or mildly crouches with most of his weight
on his rear legs. His head is slightly lowered and his ears
are laid back flat against his head, slightly pointing downward.
His tail is tucked under the belly and his muzzle is nearly
closed with his lips pulled back. The dog wants to avoid confrontation.
Active Submission Posture.
The dog acknowledges another dog or human's higher social
ranking by going into a crouching position. His head is down
or slightly pushed forward below his neck. His ears are back
and his muzzle is nearly closed with his lips pulled back.
His tail hangs down and wags slowly. The dog is submitting
itself to a higher ranking dog, human or wants to inhibit
aggression.

Passive Submission Posture.
The dog lies suppliant and calmly on the ground. His head
is down or slightly pushed forward below his neck. His ears
are back and his muzzle is nearly closed with his lips pulled
back. His tail lies on the ground, sometimes slowly wagging.
The dog is unconfident and wants to appease.

Total Submission Posture.
The dog surrenders and lies on its back. His rear legs are
spread and his tail is either tucked on his belly or laying
between his legs. Sometimes droplets of urine are released.
His ears are back and his muzzle is nearly closed with his
lips pulled back. The dog has completely surrendered.

Contact or Playful Postures.
Greeting Posture.
The dog stands or walks with his head up or moderately erect.
His tail is wagging just above his rear end. The mouth is
slightly open and relaxed. More dominant dogs have their ears
up pointing forward while younger or more submissive dogs
put their ears slightly sideways or back. The dog is friendly
and signals its readiness to establish contact.

Greeting Behavior.
A dog can display a variety of different greeting behaviors
with other dogs or humans. He is slightly bowing down and
his tail is wagging (hanging or slightly raised above his
back) in a fast, sweeping motion. His mouth is slightly open
and his ears are put back. The dogs head is lowered almost
level with his neck and nudges up frequently towards the other
dog/person. A more submissive dog may greet a more dominant
dog with a muzzle nudge or lick as an appeasement gesture.
The dog is excited and friendly.
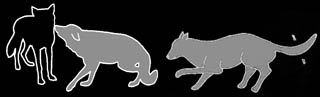
Play Solicitation Posture.
In front of his playmate, the dog lowers his front-end almost
to the ground. His forelegs are slightly spread. He moves
his head, tail and often also his back sideways in quick,
jerking motions. His mouth is slightly open and his ears are
put forward or slightly to the side. He is fixing his playmate
with his eyes. The dog invites another to play in a courtship
behavior.
Play Attack.
From the distance, the dog gazes sharply at his playmate.
He then crouches closer slowly and suddenly charges forward.
Just before he reaches his playmate, the dog stops and jumps
up or to the side. The dog ears are put forward or slightly
to the side and he does not display any hackles. His mouth
is slightly open and his tail is up or raised just slightly
above his rear. The dog shows playful activity to invite another
to play.

Body Signals
In addition to a dog's basic postures, there are a variety
of individual signals that can help you to understand the
emotional state of your dog.
Hackles (lifted hair):
- On neck and back with ears pointed forward: cautioning,
threatening
- On the lower back in the tail area: something is not right
- On the tail: intent to impress or aggression
Ears:
- Loose: calm, relaxed or disinterested
- Upright: alert, dominant, assertive
- Turned sideways: curious
- Angled back: submission, fear or invitation to play
Facial features:
- Relaxed, closed mouth: calm, relaxed, friendly or insecure
- Tense, mouth slightly open: attentive, alert
- Lips pulled up exposing some teeth, nose curled: warning,
threatening
- Lips pulled back horizontally: Insecurity, fear, submission
- Closed or slightly open mouth, lips pulled to a grin: happiness,
friendliness
Tail:
- Relaxed, down: calm, relaxed or disinterested
- Sweeping wag: excitement, happiness, greeting, socializing
- Arched high above the back: dominant, secure, alert
- Pointed backwards straight or slightly above rear: warning,
threatening
- Tucked underneath belly: fear, insecurity, submission
References:
"Der qualifizierte Hundeführer" by Manfred Müller - Oertl & Spoerer Verlag
The American Association fort he Prevention of Cruelty to Animals
<- Previous
Page | Next page -> |